Surgical microscopes have become essential tools in modern medicine, offering unmatched precision, magnification, and lighting during complex procedures. From ear surgeries to brain tumor removals, these microscopes adapt to the specific needs of each medical specialty.
In this article, we’ll explore the major applications of surgical microscopes across ENT, dental, neurosurgery, ophthalmology, plastic surgery, and more—along with the unique features and technologies required by each field.
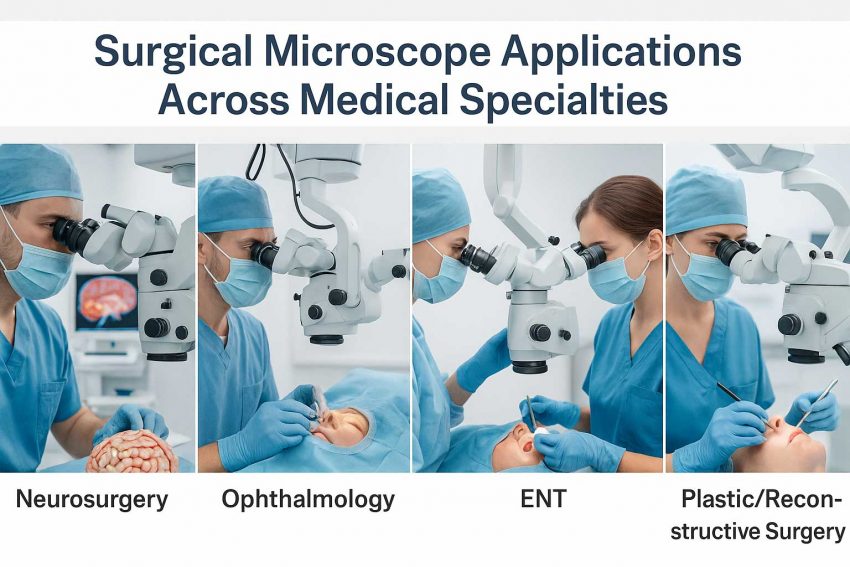
1. ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat) Surgery
ENT surgeons were among the first to adopt surgical microscopes, particularly for delicate procedures in the ear and sinus cavities.
- Common uses: Tympanoplasty, mastoidectomy, sinus surgery, stapedectomy
- Key features: Compact design, deep focal length, coaxial LED illumination, smooth arm movement
Why it matters: ENT structures are small and located in deep, narrow spaces—making high-resolution imaging and accurate instrument tracking essential.
2. Dentistry and Endodontics
Dental specialists use surgical microscopes to enhance visibility and improve precision, particularly in root canal and cosmetic procedures.
- Common uses: Root canal therapy, crown placement, restorations, smile design
- Key features: Excellent depth of field, ergonomic design, adjustable angle viewing, HD camera integration
Why it matters: Better visualization leads to more precise treatment, reduced retreatment rates, and enhanced patient outcomes.
3. Neurosurgery
Neurosurgical procedures demand the highest level of magnification, clarity, and control—especially when working near critical structures in the brain or spine.
- Common uses: Tumor resection, spinal decompression, vascular microsurgery, aneurysm clipping
- Key features: Robotic arms, AR overlays, motorized zoom/focus, high-resolution optics, long working distance
Why it matters: A single millimeter makes a difference in neurosurgery. Microscope precision improves safety and surgical outcomes.
4. Ophthalmology
Surgical microscopes are vital in eye surgeries that require ultra-fine visualization of corneal, lens, and retinal structures.
- Common uses: Cataract surgery, retinal detachment repair, corneal transplant, glaucoma treatment
- Key features: Crystal-clear magnification, smooth focus, intraoperative OCT, footswitch control, integrated video
Why it matters: Eye structures are transparent and fragile—demanding consistent illumination and contrast clarity without glare.
5. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Microsurgical techniques in plastic surgery often require magnification for tasks such as vessel repair, tissue flaps, and grafting.
- Common uses: Free flap surgery, breast reconstruction, reattachment of digits, facial reconstruction
- Key features: Wide field of view, 3D optics, mobility, excellent hand–eye coordination support
Why it matters: Accurate micro-anastomosis is vital in reconstructive work to ensure tissue survival and natural appearance.
6. Veterinary Surgery
Microscopes are increasingly used in veterinary specialties, especially for small animal surgery, ophthalmic treatments, and dental procedures.
- Common uses: Corneal repair, tumor excision, microsutures in exotic animals
- Key features: Compact units, low-light operation, flexible positioning, veterinary-safe mounts
Why it matters: Small animals require the same level of precision as human patients in many cases.
Comparison Table: Surgical Microscopes by Specialty
| Specialty | Use Case | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| ENT | Ear, sinus, vocal cord surgeries | Compact size, long reach, coaxial light |
| Dental | Root canal, aesthetic work | Ergonomic, tilt view, HD camera |
| Neurosurgery | Brain, spine, tumor resection | Motorized zoom, AR, long working distance |
| Ophthalmology | Cataract, retina, corneal repair | High clarity, smooth focus, intraoperative imaging |
| Plastic Surgery | Flaps, microvascular repairs | 3D view, wide field, portable base |
| Veterinary | Ophthalmic, dental, soft tissue | Compact, portable, low-light optics |
Final Thoughts
Surgical microscopes have evolved into indispensable tools across many fields. By understanding how they function in different specialties, surgeons and healthcare providers can better select the right features and configurations for their daily needs.
Whether you’re a dental surgeon performing root canals or a neurosurgeon removing tumors, choosing the right surgical microscope ensures better precision, safety, and outcomes.
Explore more in our brand and buyer’s guides to compare models that match your specialty best.